What is machine learning and how can it be used?
Perhaps you know the feeling: you open Netflix and immediately find a series that suits your taste perfectly. Or your smartphone sorts your photos so cleverly that you can find certain moments with just one tap. You might be thinking: "That's pretty handy." And that's exactly what machine learning is all about. Machine learning has evolved from a science fiction concept to a central component of today's information processing.
Machine learning is no longer a future scenario, but accompanies you every day - inconspicuously, but incredibly effectively. It helps you to save time, make better decisions and get information that suits your needs. And the more you engage with it, the more you realize how much this technology is changing our world.
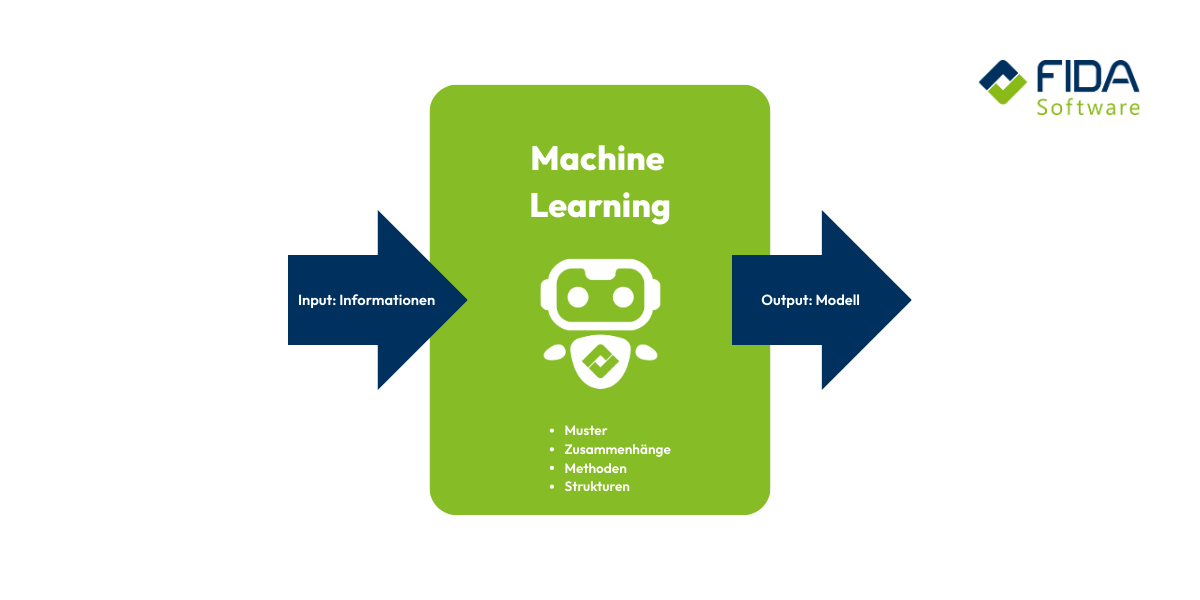
What makes machine learning so special? Computers learn things without having to be told every single step. The algorithms run on computers, process large amounts of data and automate tasks by recognizing patterns and making decisions. They recognize patterns, make predictions and thus accelerate business processes. And this not only opens up new possibilities for you in your everyday life, but above all for companies - large and small. Processes run more smoothly, data is used in a more valuable way and tasks that used to take up a lot of time are now performed by a system almost incidentally - although the exact task is decisive in determining which machine learning model is used.
Join us on a journey behind the scenes of artificial intelligence in this article.
What does machine learning actually mean?
If you've ever wondered how computers manage to get smarter from experience, then machine learning is the right topic for you. Machine learning (ML for short) is a sub-area of artificial intelligence. These terms are often used together, so it is important to differentiate between the individual terms such as machine learning, deep learning and AI. The aim is to develop systems that learn from data, recognize patterns and improve themselves over time without anyone having to program every single step.
Artificial intelligence is therefore the overarching term. It describes technologies that attempt to emulate human thinking - whether through firmly defined rules or learning algorithms. This is why AI and machine learning are often mentioned in the same sentence, even if they are not the same thing. The definition of machine learning forms an important basis for understanding the terms and correlations within artificial intelligence.
You can remember it like this: Machine learning is a special approach within AI - but not every AI works with machine learning.
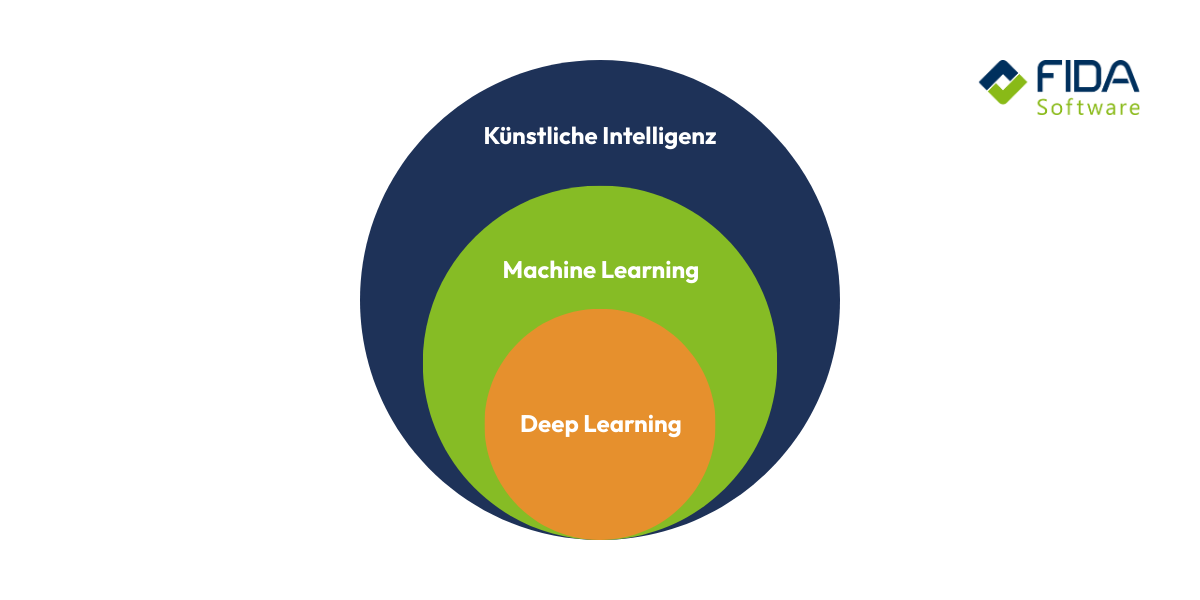
Machine learning vs. deep learning - what's the difference?
You may have noticed that the terms machine learning and deep learning are often used interchangeably in everyday life. No wonder, because both are part of artificial intelligence. Nevertheless, there are important differences that will help you to better classify the technology.
Basically, you can imagine the relationship like this: Machine learning is the big umbrella term - which includes neural networks - and deep learning is in turn a special area of these neural networks. Deep learning is a sub-area of machine learning that is characterized by particularly complex structures and large amounts of data.
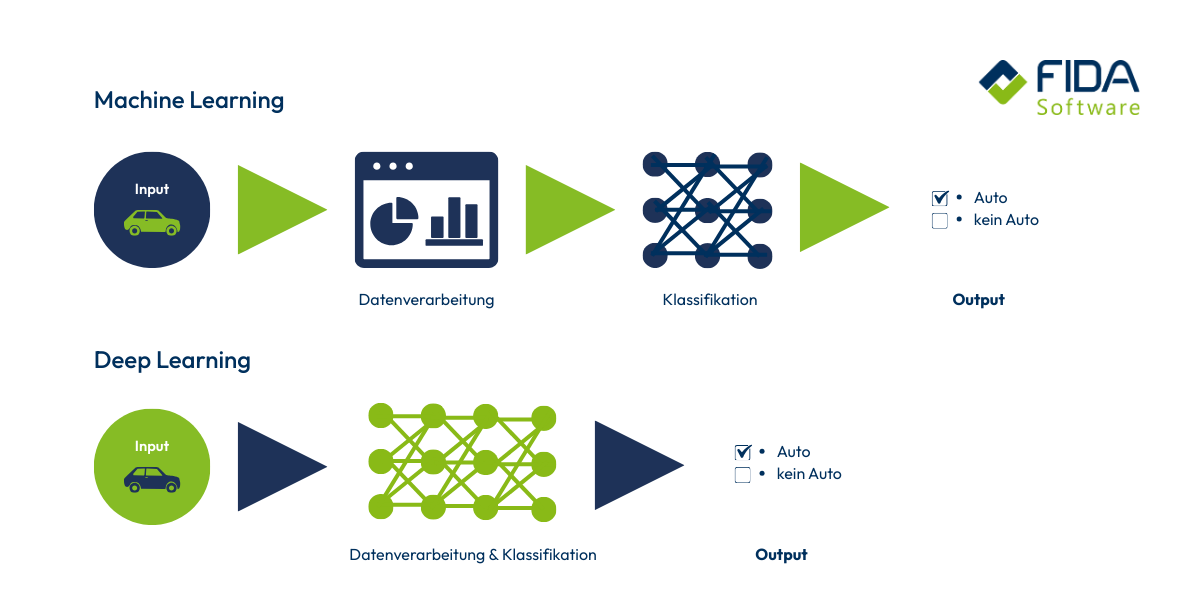
How does machine learning work?
Machine learning basically works in a similar way to your own learning process: the system gets better and better over time through repetition, trial and error and feedback. In the beginning, the algorithm still receives support from humans or from a cleanly curated data set - later it makes decisions independently. The process can be easily divided into a few steps.
In the so-called machine learning process, the individual phases - from data collection, model development and training through to optimization and implementation - are systematically run through. The machine learning process requires a large amount of high-quality data in order to achieve precise results.
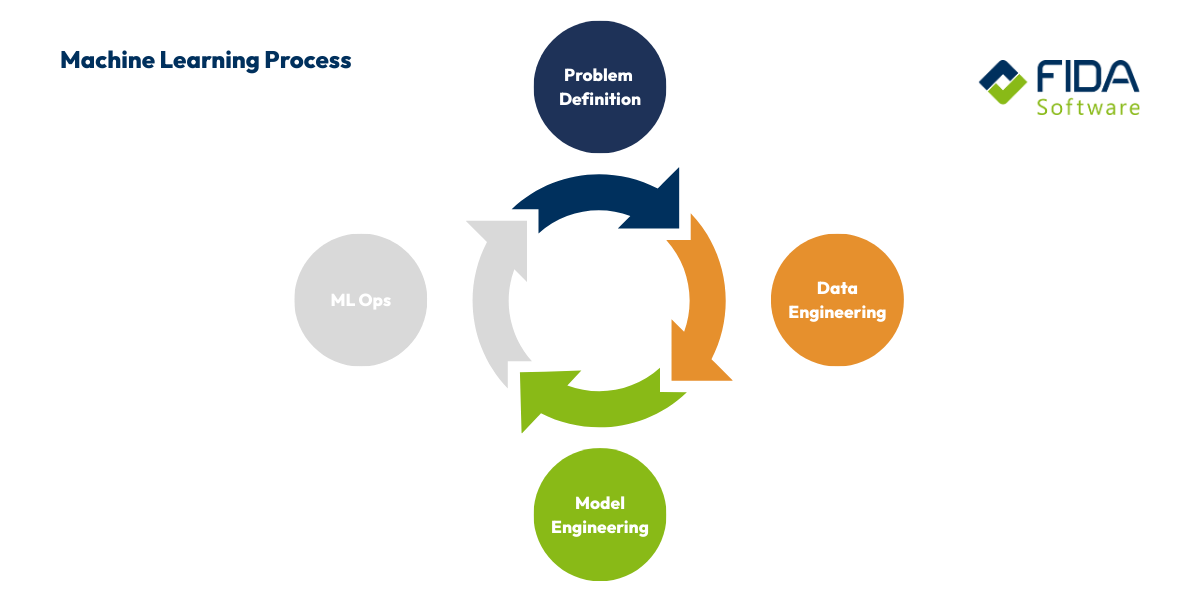
1st training: The system learns from examples
First, you feed the model with a training data set. Large data sets are crucial here, as they form the basis for training and optimizing machine learning models. This data comes from you or your team and helps the algorithm to recognize patterns, correlations and rules. The more and the more diverse the examples are, the better the system can work later on.
The quality and quantity of the data sets are decisive for the performance of the model. Individual data points are used to refine the model in a targeted manner and enable more precise predictions. Sample data plays a central role in training various learning methods, as it helps the model to recognize relevant patterns. The amount of data significantly influences the accuracy and training of the model. In machine learning, large amounts of data are often processed in order to continuously improve the models and enable automated processes.
You can think of this step as "practicing": With each run, the quality of the results improves.
2 Iterative learning: step by step to better accuracy
Machine learning is an ongoing process. The model repeats its tasks until it reaches a certain level of accuracy. In this phase, the performance of the system is continuously monitored. If necessary, you can intervene, readjust or provide additional data to further improve the results. Human intervention is crucial to monitor and optimize the training process to ensure the quality and accuracy of the models on an ongoing basis.
3. detect and correct errors
If the model makes an incorrect prediction, this error is used to further adapt the system. The internal parameters change - this is how the model adapts its "way of thinking".
With each correction, it becomes a little more precise and learns to reliably recognize the correct patterns, whereby it is increasingly able to recognize complex patterns.
4th use: The model works independently
As soon as the accuracy is high enough, you can use the model in practice. The ML model analyzes new data, recognizes patterns and thus supports well-founded decisions in the respective business processes. It can now handle new, previously unknown data and independently make predictions or support decisions. The system uses its learned knowledge to react in real time and deliver ever better results.
What types of machine learning are there?
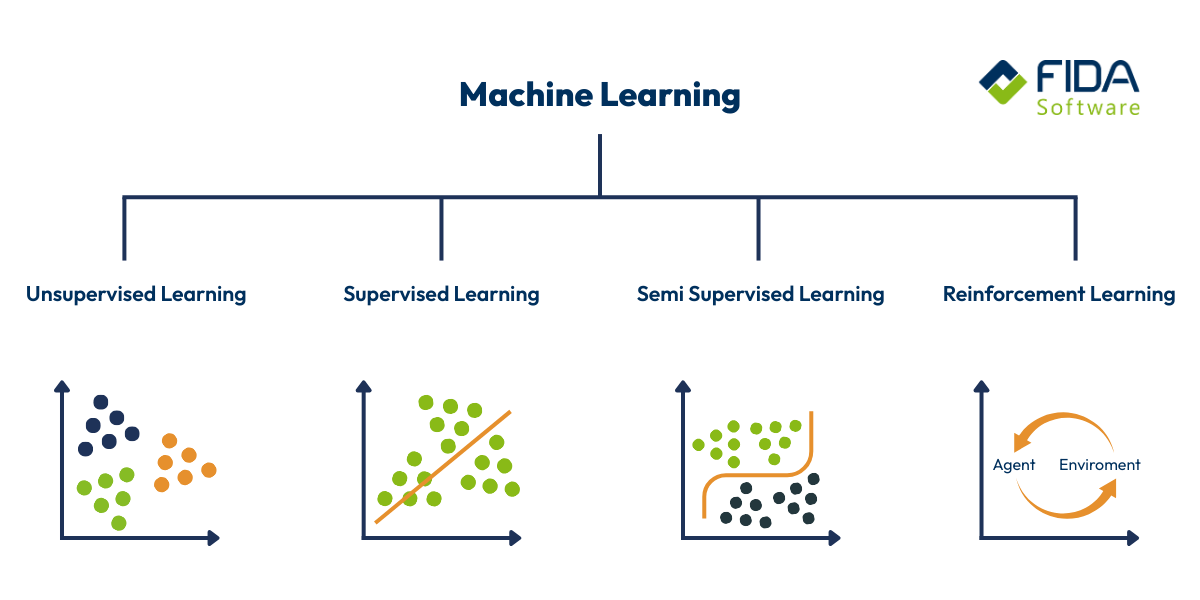
Not all machine learning is the same. There are different approaches that have very different strengths depending on the objective, data situation and effort involved. These approaches can take different forms of machine learning, each offering specific applications and benefits for different industries. To give you a better sense of which approach is suitable for what, let's take a closer look at the four main types.
Supervised learning
In supervised learning, the algorithm is given a kind of "learning aid": the data you feed it with is already labeled. Various learning methods and machine learning algorithms are used to develop the optimal model for the task at hand.
A typical example is a spam filter. Here, the model learns from many emails that have already been marked as "spam" or "non-spam", whereby the model is trained to make predictions that are as accurate as possible. The model plays a central role in the analysis and categorization of the data by recognizing patterns and using these for future decisions.
Importantly, the training data must be representative of the real world. If the data only contains idealized examples and shows no natural variance, the model does not learn reality comprehensively enough. There is also a risk of overfitting if the model is too complex: the model then learns the training data virtually by heart, but cannot apply the knowledge to new, unknown emails.
Application examples:
E-mail filtering: Classification of e-mails as spam or non-spam.
Medical diagnostics: Predicting illnesses based on symptoms.
Financial analysis: Prediction of share prices.
Image recognition: identification of objects in images.
Unsupervised learning
In unsupervised learning, the algorithm is completely on its own. You give it unlabeled data - with no right or wrong answers - and it tries to recognize patterns and correlations on its own. Understanding the relationships between variables is crucial in order to extract relevant information from the data.
Various models and methods are used to gain new insights from unstructured data and make correlations visible. The practical application of unsupervised learning can be seen, for example, in companies that use it to optimize processes or in everyday life, such as in the automatic sorting of photos.
The approach is particularly suitable for forming groups (clusters) or identifying unusual patterns (anomalies). Recommendation functions in stores often work with it. For example, they recognize: "Customers who bought this product are also interested in ..."
Unsupervised learning is also very valuable for fraud detection. If the system detects patterns that deviate significantly from the norm, it sounds the alarm.
Application examples:
Shopping basket analysis: discovering products that are frequently bought together.
Genetic clustering: Grouping of genes with similar expression patterns.
Social network analysis: Identification of communities within large networks.
Anomaly detection: Detecting fraudulent transactions in banking.
Semi-Supervised Learning
Maybe you know the problem: You have a lot of data, but only a small part of it is labeled - and labeling everything completely would be far too time-consuming. The amount of data available plays a decisive role in the efficiency of semi-supervised learning, as the aim is to achieve the greatest possible benefit with limited resources. This is exactly what semi-supervised learning is for.
In semi-supervised learning, certain requirements must be met by the ML models, for example with regard to the ability to deal with incomplete or heterogeneous data and to take industry-specific requirements into account.
A mix of both worlds is used here:
First, the model learns with the existing labeled data.
It then uses this knowledge to classify unlabeled data.
If it recognizes patterns with a high degree of certainty, this data is "pseudo-labeled" and included in the training set.
ML models play a central role here, as they are able to recognize patterns in unlabeled data and classify them efficiently.
In this way, the data set grows step by step and the model becomes more and more precise - without you having to prepare all the data manually.
Reinforcement learning
Reinforcement learning works like learning through experience. The algorithm tries something out, receives feedback - positive or negative - and optimizes its behaviour. The algorithm performs various actions in order to achieve the best possible result. In the learning process, decisions are continuously made to solve complex problems, with the algorithm learning from the results of its actions. In some cases, human intervention may be required, for example to adjust the data or optimize the model to address specific problems. It gets better with each run.
The special feature: The system does not just pursue short-term results, but works towards an overarching goal. One example is a chess program. It can make sense to temporarily sacrifice pieces in order to win the game later. It is precisely this long-term thinking that reinforcement learning masters particularly well.
It is suitable wherever complex decisions have to be made in dynamic environments - for example in robotics or autonomous systems.
Application examples:
Video games: teaching artificial intelligence to play complex video games and achieve outstanding performance.
Robotics: enabling robots to learn tasks such as walking or grasping objects.
Autonomous vehicles: Developing systems for self-driving cars that can make decisions in real traffic.
Personalized recommendations: We adapt suggestions over time to users' individual preferences.

Common algorithms in machine learning - an overview
If you want to start a machine learning project, you will quickly realize that there is a large selection of algorithms. Each of them has certain strengths and is suitable for different tasks. There is a wide range of machine learning algorithms that can be used depending on the application. Depending on the task, different methods and models are used that are specifically tailored to the respective requirements. Machine learning plays a central role here and opens up numerous possibilities for various topics and areas of application. The following methods are among the most frequently used - and will give you a good initial overview.
Neural networks
Artificial neural networks (ANN) are modeled on the structure of the human brain. They consist of thousands of interconnected nodes (neurons) that are organized in several layers:
Input layer: records the raw data (e.g. the pixels of an image).
Hidden layers: This is where the actual "intelligence" takes place. Each layer filters out more complex features - from simple lines to entire faces.
Output layer: Provides the result (e.g. "The image shows a cat").
The special feature: This layered structure allows neural networks to process unstructured data that would be too much for conventional algorithms. The more layers a network has, the more complex relationships it understands - this is known as deep learning.
Areas of application:
Computer vision: facial recognition or medical image analysis.
NLP (Natural Language Processing): Translation tools and chatbots such as ChatGPT.
Generative AI: Creation of realistic images, music or texts.
Linear regression
Linear regression is one of the simplest and most reliable approaches when it comes to predicting numerical values.
For example, you could use it to estimate real estate prices based on historical data for a specific area. The algorithm looks for a linear relationship between different factors - and uses this to create forecasts. The method follows a clearly defined mathematical rule that specifies how the individual influencing variables are combined to make a prediction.
Logistic regression
Logistic regression is also one of the classic methods in supervised learning. It makes predictions for categories - i.e. answers such as "yes" or "no".
Typical areas of application are spam detection, quality checks or all situations in which data needs to be categorized into clearly defined classes.
Clustering
Clustering is a technique from unsupervised learning. The algorithm independently searches for patterns and forms groups (clusters) without you giving it any instructions beforehand.
This helps to recognize structures or detect unusual data points - things that often escape the human eye. Clustering is frequently used in data analysis or customer segmentation in particular.
Decision trees
As the name suggests, a decision tree works with a series of successive decisions that branch out like branches of a tree.
It can predict numerical values as well as classify data into categories. This is a major advantage over neural networks: Decision trees are easy to understand and explain. This means you can clearly see why the model came to a certain result.
Random forests
A random forest is, so to speak, a "team" of many decision trees. Each tree makes its own prediction - and in the end an overall judgment is formed from all the results.
This combination improves accuracy and reduces the risk of a single tree making incorrect decisions.
What are the areas of application for machine learning?
Machine learning is extremely versatile and is used in many industries and areas of life. Different methods and algorithms are used depending on the objective. Here is an overview of the most important areas:
1. marketing and sales
In marketing, machine learning helps to better understand customers and create personalized offers. Algorithms analyze buying behavior, interests and preferences in order to create suitable recommendations or targeted campaigns. On online shopping platforms, for example, you will receive suggestions such as "Customers who bought this product also bought ...". For companies, this means higher customer satisfaction and more effective marketing measures.
Examples
Recommendation engines: suggestions such as "Customers who bought this product also bought ..."
Cross-selling strategies: personalized product recommendations during the ordering process
2. customer service
Chatbots and digital assistants, which you may already be using on websites or in apps, often work with machine learning. They learn from previous inquiries, can answer routine questions independently and forward more complex requests to humans. This saves time, reduces waiting times for customers and relieves employees.
Examples
Chatbots and virtual assistants: Answering FAQs, personalized advice, forwarding complex queries to human employees
Speech recognition / voice assistants: Automated interaction via devices such as Siri or voice bots
3. finance and banking
Machine learning has become indispensable in the world of finance. Algorithms recognize unusual transactions and thus help to detect attempted fraud at an early stage. At the same time, they support risk analysis, for example with loan applications, and improve the prediction of share prices or market trends.
Examples
Fraud detection: analysis of transactions, detection of suspicious activities
Automated share trading: high-frequency trading and portfolio optimization
4. production and logistics
In industry, machine learning ensures more efficient processes. Algorithms can predict machine maintenance requirements, optimize production processes and plan supply chains more intelligently. This can cut costs, reduce downtime and make better use of resources.
Examples
Robotic process automation (RPA): Automation of recurring manual tasks
Predictive maintenance: prediction of maintenance requirements for machines
Optimization of supply chains: more efficient planning and use of resources
5. healthcare
Machine learning also has enormous potential in the medical sector. Systems analyze medical images, assist with diagnoses or recognize patterns in patient data in order to identify diseases at an early stage. This enables doctors to make decisions more quickly and improve care.
Examples
Computer vision for medical images: Support with diagnoses, pattern recognition in patient data
6 Everyday life and entertainment
You also encounter machine learning in everyday life, often without realizing it: Music and video recommendations from streaming services, facial recognition in smartphones, smart home applications or navigation systems - all of these are based on algorithms that learn from data to offer you better and more personalized services.
Examples
Streaming recommendations: Music and video recommendations on platforms such as Spotify or Netflix
Facial recognition and smart home applications: Smartphones, door sensors, intelligent devices
Navigation systems: route optimization and traffic forecasts
Conclusion: Machine learning - your entry into the future
Machine learning is no longer a topic for the future - it is part of our everyday lives and is changing how companies work, offer products and make decisions. From personalized product recommendations and automated customer support to fraud detection and medical diagnoses: the possible applications are diverse and go far beyond the familiar examples.
For you personally or for your company, this means that anyone who is familiar with machine learning can make processes more efficient, make better decisions and develop innovative solutions. It is not necessary to be an expert straight away. You can learn the basics step by step, understand the various algorithms and try out practical applications.
The FIDAcademy offers exactly the right courses for this. Whether you want to understand the basics of machine learning, get to know deep learning or implement specific applications such as recommendation engines, chatbots or predictive maintenance - at the Academy you will find practical training courses that will help you to use machine learning in a targeted manner. This way, you can enter the world of artificial intelligence in a safe and structured way and make the most of the opportunities offered by this technology.
FAQ: Frequently asked questions about machine learning
Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence. Computers learn from data and improve with every new experience - just like humans. The aim is to recognize patterns, make predictions or automate decisions without every rule having to be programmed by a human beforehand.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the overarching term and describes any technology that imitates human intelligence.
Machine learning is a part of this - it is the method by which systems learn independently from data.
In short: ML is a subcategory of AI, but not all AI uses machine learning.
Yes - but with a little twist:
ChatGPT is based on an advanced machine learning model, the so-called Large Language Model (LLM). This was trained with huge amounts of text in order to recognize patterns in language and formulate comprehensible answers.
You can therefore think of ChatGPT as a particularly powerful application of machine learning.
There are many examples that you use every day without consciously thinking about them. A typical example: recommendations from Netflix, Amazon or Spotify.
These services analyze your behavior - such as what you have bought, listened to or watched - and suggest suitable products, films or songs.
Spam filters, navigation systems or photo tagging in smartphones are also part of this.
Not necessarily. You can understand the basics even without programming experience. Many tools now make it very easy to get started. However, if you want to develop your own models, some programming - usually in Python - is necessary.
Companies use ML for example for
personalized advertising and product recommendations
automated customer service
fraud detection
production optimization and predictive maintenance
risk analysis
process automation
The possibilities are constantly growing.
Absolutely - and it's easier than many people think. With good instructions, you can quickly understand the basics and try out your first models. At the FIDAcademy, you will find practical courses that will guide you step by step - from beginner to professional.